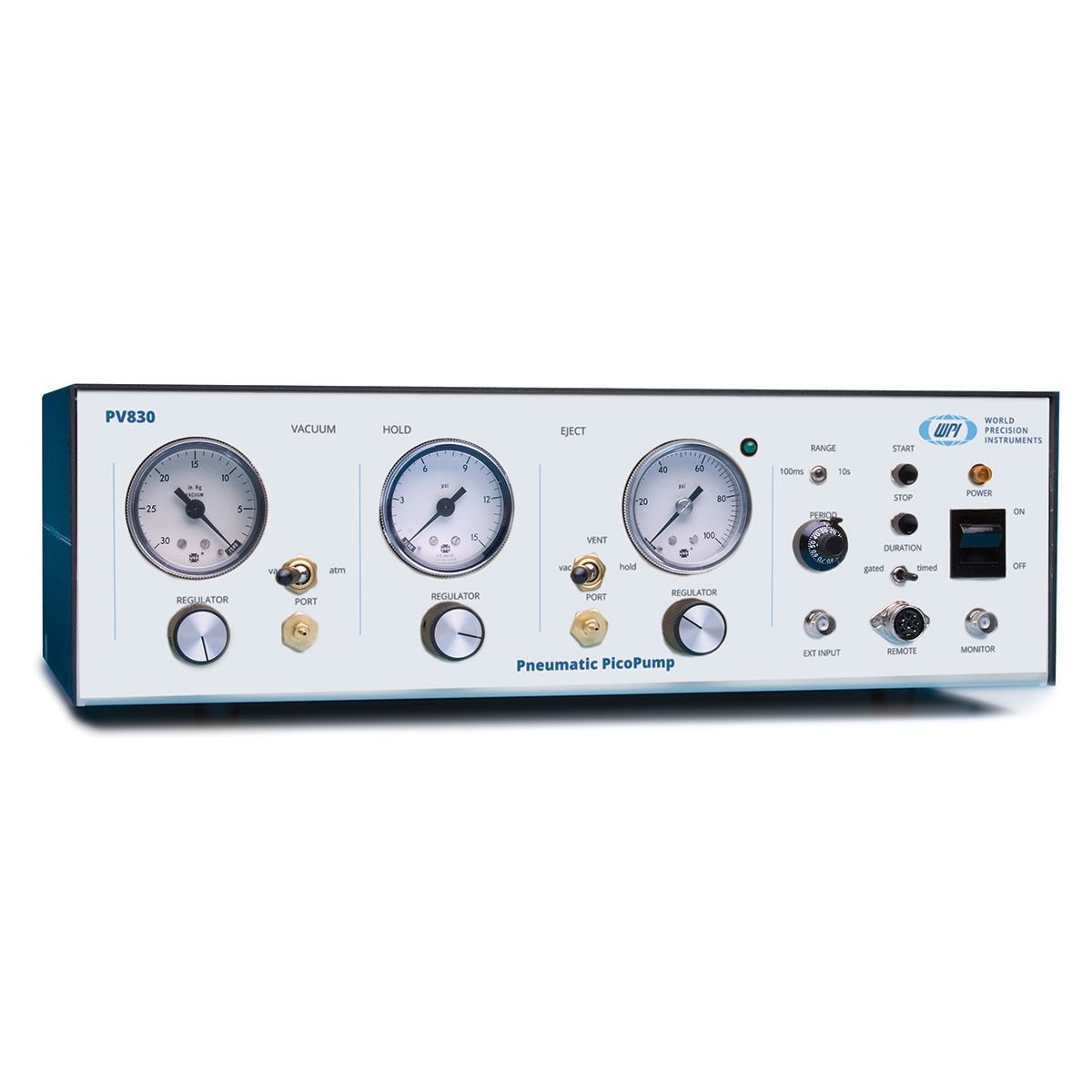
气动皮升操作泵
仪器概况
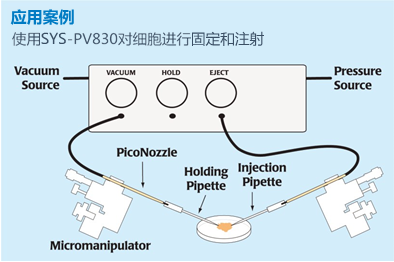
WPI 公司的气动皮升泵通过使用调节的气压来固定细胞并注射液体,是斑马鱼显微注射及斑马鱼卵细胞基因感染实验中经典的注射系统。具有使用方便, 注射程序简单,重复性极佳的优点,注射的体积范围从pL到nL不等。正压和负压由单独的端口提供,正压主要用于高压喷射,负压用于吸附支持细胞及毛细管尖端的充液,第二个压力端口在每次注射脉冲之间让毛细管尖端保持低的正性维持压,以阻止液体通过毛细管虹吸作用或扩散的方式回吸。
定时作用、喷射压力、维持压和吸附作用都是独立地通过仪器前板的控制旋钮和显示表来调节,注射压通过前板的20圈调节器控制,内置定时电路可以精确控制当注射压力应用到输出端口的时间参数。注射压力间隔可以从前板手动触发,也可以通过脚踏开关或计算机控制的TTL脉冲触发,一个5V的输出为计算机或其它监测设备提供一个逻辑电平脉冲。
SYS-PV830可以通过前板的各自调节器提供喷射压、维持压和真空。喷射压用来提供高压脉冲注射液体、维持压主要用来防止毛细管虹吸导致液体尖端回吸。真空也通过前板以同样的方式调节。真空端口可以在前板用棒状开关从真空切换到大气环境、真空可以引导到喷射端口。


产品特征
● 操作简便
手动控制:轻按前面板启动键开始或停止
脚踏开关:脚踏开关灵活控制开始或停止
外部输入:通过计算机编程控制时间参数或TTL信号启动
● 双重模式
外部启动:通过计算机控制启动时间
内部启动:通过仪器内部晶体振荡器控制启动时间
● 计量准确
时间参数:具有100ms和10s两个时间档,能够精确调节到0.2ms
体积准确:通过调节注射时间、注射压和毛细管尖端大小均可确保注射体积一致
● 可重复性
通过固定压力、时间和尖端口径,可确保每次注射体积一致,做到可重复性

产品用途
用于斑马鱼研究:
● 用于斑马鱼卵细胞DNA等遗传物质注射;
● 用于斑马鱼幼鱼体内药物、染料的微量注射; 用于斑马鱼幼鱼体内肿瘤细胞及其它干细胞 的种植;
用于昆虫研究:
● 用于果绳卵细胞DNA等遗传物质注射;
● 用于棉铃虫、褐飞虱等蚕蛹体内药物及染料等微量注射;
用于嗅觉或味觉研究:
● 用过PUFF方式对神经元或脑内核团给刺激物或气味;
用于物质的转移:
● 用于细胞核或细胞器移植; 用于微小粒子的移取;
PV800系列气动皮升操作泵参考文献
[1] Operant conditioning paradigm for juxtacellular recordings in functionally identified cortical neurons during motor execution in head-fixed rats
Journal of Neuroscience Methods 2020, 329, 108454 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2019.108454
[2] Characterization of immune response against Mycobacterium marinum infection in the main hematopoietic organ of adult zebrafish (Danio rerio)
Developmental & Comparative Immunology 2020, 103, 103523 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dci.2019.103523
[3] Inhibition of amyloid beta toxicity in zebrafish with a chaperone-gold nanoparticle dual strategy Nature Communications 2019, 10, 3780
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11762-0
[4] High-resolution 3D imaging and analysis of axon regeneration in unsectioned spinal cord with or without tissue clearing
Nature Protocols 2019, 14: 1235–1260 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-019-0140-z
[5] Dimethyl Fumarate Reduces Microglia Functional Response to Tissue Damage and Favors Brain Iron Homeostasis Neuroscience 2019, November, in press.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.10.041
[6] Loss-of-function of sox3 causes follicle development retardation and reduces fecundity in zebrafish Protein & Cell 2019, 10(5):347–364
https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-018-0603-y
[7] Location and Plasticity of the Sodium Spike Initiation Zone in Nociceptive Terminals In Vivo Neuron 2019, 102(4):801-812.e5
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2019.03.005
[8] In Vivo Force Application Reveals a Fast Tissue Softening and External Friction Increase during Early Embryogenesis Current Biology 2019, 29(9):1564-1571.e6
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2019.04.010
[9] Active membrane conductances and morphology of a collision detection neuron broaden its impedance profile and improve discrimination of input synchrony
Journal of Neurophysiology 2019, 122(2):691-706 https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00048.2019
[10] Zebrafish as a predictive screening model to assess macrophage clearance of liposomes in vivo Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine 2019, 17:82-93 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2018.11.017
[11] Wnts control membrane potential in mammalian cancer cells The Journal of Physiology 2019, 597(24):5899-5914 https://doi.org/10.1113/JP278661
[12] Orexin facilitates GABAergic IPSCs via postsynaptic OX1 receptors coupling to the intracellular PKC signalling cascade in the rat cerebral cortex
Neuropharmacology 2019, 149:97-112 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.02.012
[13] Central nucleus of the amygdala is involved in induction of yawning response in rats Behavioural Brain Research 2019, 371, 111974 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2019.111974
[14] Oxytocin Receptors Are Expressed by Glutamatergic Prefrontal Cortical Neurons That Selectively Modulate Social Recognition
Journal of Neuroscience 2019, 39 (17):3249-3263; https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2944-18.2019
[15] Optimization-by-design of hepatotropic lipid nanoparticles targeting the sodium-taurocholate cotransporting poly
-peptide
eLife. 2019; 8: e42276.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.42276
[16] Circulating tumor cells exit circulation while maintaining multicellularity, augmenting metastatic potential Journal of Cell Science 2019, 132:jcs231563
https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.231563
[17] Intelectin 3 is dispensable for resistance against a mycobacterial infection in zebrafish (Danio rerio)
Scientific Reports 2019, 9, 995 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-37678-1
[18] The C-terminal tails of endogenous GluA1 and GluA2 differentially contribute to hippocampal synaptic plasticity and learning
Nature Neuroscience 2018, 21:50-62
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-017-0030-z
[19] Application and optimization of CRISPR–Cas9-mediated genome engineering in axolotl (Ambystoma mexicanum)
Nature Protocols 2018, 13: 2908–2943 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-018-0071-0
[20] Engaging and disengaging recurrent inhibition coincides with sensing and unsensing of a sensory stimulus Nature Communications 2017, 8, 15413
https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15413
[21] Origins of Cell-Type-Specific Olfactory Processing in the Drosophila Mushroom Body Circuit Neuron. 2017, 95 : 357–367
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2017.06.039
[22] A Population of Projection Neurons that Inhibits the Lateral Horn but Excites the Antennal Lobe through Chemical Synapses in Drosophila
Front Neural Circuits. 2017; 11: 30. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncir.2017.00030
[23] Cell-Specific PKM Isoforms Contribute to the Maintenance of Different Forms of Persistent Long-Term Synaptic Plasticity
Journal of Neuroscience 2017, 37 (10) 2746-2763; https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2805-16.2017
[24] Nicotinic activity depresses synaptic potentiation in layer V pyramidal neurons of mouse insular cortex Neuroscience 2017, 358 : 13-27
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.06.031
[25] D-serine released by astrocytes in brainstem regulates breathing response to CO2 levels Nature Communications 2017, 8, 838
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00960-3
[26] A high-throughput functional genomics workflow based on CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeted mutagenesis in zebrafish Nature Protocols 2016, 11, 2357–2375
https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2016.141
[27] Neuroinflammatory TNFα Impairs Memory via Astrocyte Signaling Cell 2015, 163(7):1730-1741 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.11.023










